本文聊聊服务端系统设计中,关于用户敏感数据相关的设计。
密码安全
对于大部分的网络服务来说,都是注册登录之后才能使用。在注册成功后,服务端需要保存用户的账号和密码,这样后续才能验证用户登录是否合法。
MD5处理
最常见的加密方式,一般就是将用户密码进行一次 MD5 处理:
1 | DigestUtils.md5Hex("123456") // e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e |
这时,存入数据库中的就不是明文密码了,而是 MD5 处理后的密码摘要。
MD5 摘要算法决定了无法根据摘要信息推算出原始数据,但仍然不安全。从攻击者角度来说,虽然 MD5 无法逆向计算,但是理论上可以根据正向计算,组合所有字符构建出一张大表(一般将这张表称为彩虹表),拿到密码摘要后,从彩虹表中反查,即可获取到用户的原始密码。
在 CMD5 查询,以上面的密码为例,不用多久就能查到原始密码:
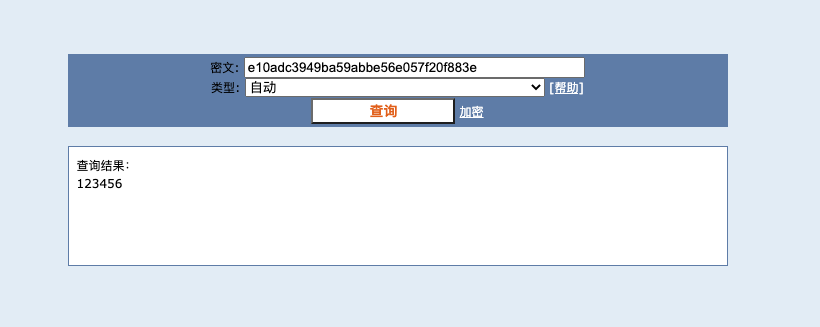
加盐处理
在进行 MD5 前对密码加盐是一种常见的操作,但是需要注意,盐不要固定,并且需要有一定长度。
假设盐是固定的简单字符串:
1 | // 假设密码为123456,盐为abc |
通过查询可以 df10ef8509dc176d733d59549e7dbfaf 找到对应的原始字符串为 123456abc。
那如何判断是否有加盐呢?通过注册一个新账号,使用简单密码进行注册,比如 1,服务端 MD5 处理后得到的最终密码摘要为 e511341dc05782269d3d859b5ff3939b,反查之后,就可以得出盐为 abc :
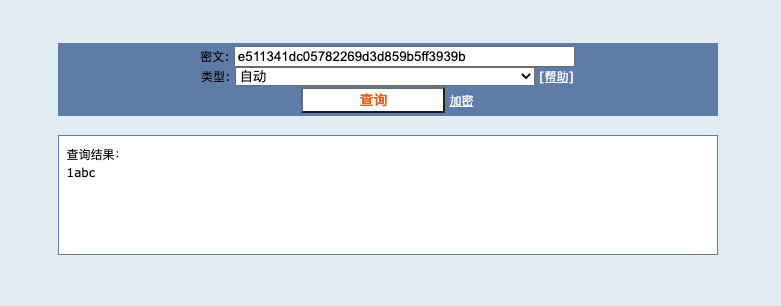
因为使用了简单的并且是固定的盐,意味着如果用户的原始密码就简单,那拼接后的字符串也简单,那么一般从彩虹表中都能找到,进而可以推断出原始密码。
同时使用相同的盐,意味着相同密码的用户的 MD5 是一样的,那么只要知道一个,就可以获取多个用户的密码。
因此推荐每个用户的盐不一样,并且要长一点,例如使用 UUID。因为对于攻击者来说,即使拿到了所有用户的密码和盐,也加大了分析出每个用户的原始密码的成本。
使用BCrypt算法
也推荐使用其他算法,如 BCrypt 就是为了加密而设计的算法:
使用示例:
1 | <dependency> |
1 | String password = "123456"; |
身份敏感信息
身份敏感信息是指像用户姓名,身份证号等信息,像这种信息,我们不能使用密码加密那种单向算法,因为无法解密。这时候应该选择可逆算法,包括对称加密和非对称加密算法。
对称加密算法,是指双方使用相同的密钥进行加密和解密,特点是加密速度快,但是密钥在传输过程中可能会被窃取,如 AES,DES 就属于此类。
非对称加密算法,是指使用密钥对进行加密和解密,具体来说,就是使用公钥加密,使用私钥解密,公钥可以公开(可以发送给请求方,请求方使用公钥加密信息),私钥不能公开(接收方使用私钥解密信息)。特点是加密速度比较慢,但是可以避免密钥传输过程的安全问题,如 RSA 就属于此类。
因为我们是属于服务内部使用,不存在分发密钥的情况,所以更偏向于使用对称加密,此处使用AES算法对敏感信息做加密,而AES算法又有几种加密模式:ECB、CBC、CTR、OCF、CFB、XTS。
使用ECB模式
ECB模式是最简单的块密码加密模式,加密前根据加密块大小分成若干块,之后将每块使用相同的密钥单独加密,解密同理。因为使用相同的数据块密钥加密后的密文相同,所以会有安全问题。
如果我们将密文重复几次,可以发现仍然可以解密成功,结果明文被复制了多次:
1 | String key = "77fe5145ef3749a4"; |
因此如果有个密文是由多个子密文拼接而成的 AES(A) + AES(B) + AES(C),即使我们不知道密钥,也可以通过调换子密文位置,使业务逻辑出错。
使用CBC模式
CBC模式先将明文切分组,每一组与上一组的密文块进行异或运算后,再使用密钥进行加密。第一个块需要使用初始化向量(IV),之后的分组使用前一个分组的数据,这样即使明文一样,加密后的数据也是不同。因为需要保证分组访问的顺序性,相较ECB提高了安全性,但是加密过程无法并行化,而且消息必须填充到分组大小的整数倍。
如果再将密文复制多次,发现无法解析出明文:
1 | String key = "77fe5145ef3749a4"; |
示例
对于敏感数据保存,可以使用 AES+CBC 加密保存。在数据库设计上,不要直接存储用户的明文信息,而存储密文信息以及数据脱敏信息,这样做普通查询的时候,直接使用脱敏信息即可。密钥和初始化向量最好是独立唯一并且变化的,并且使用独立的加密服务来保存密钥和加密操作。
以用户姓名和身份证为例:
1 |
|
同时,还需要记录密钥和初始向量信息:
1 |
|
加密服务使用 GCM 模式的 AES-256 对称加密算法,加密时允许传入一个 AAD 用于认证(当解密时使用的 AAD 错误时,依然会解密失败):
1 |
|
上层接口调用:
1 | ("save") |
调用加密接口后可以看到用户信息已经脱敏:
1 | { |
而调用解密接口可以看到原始信息:
1 | { |
如果 AAD 信息不对,将返回 Tag mismatch!
日志过滤
除开数据库外,另一个可能会存储敏感数据的地方就是日志。
一般来说,日志打印数据有两种情况:
敏感信息在参数中,如:
1
2String password = "123456";
log.info("user password: {}", password);这种情况方便处理,在写入日志之前先处理:
1
2String password = "123456";
log.info("user password: `{}`.", DesensitizationUtils.desensitize(password);敏感信息在对象中,如:
1
2
3User user1 = new User();
user1.setPassword("123456");
log.info("user: `{}`.", user1);这种情况下,因为最终是以字符串的形式写入文件的,因此可以在写入文件之前对字符串进行处理。
示例
以 Logback 为例,可以通过自定义 PatternLayout 来实现:
1 | public class DesensitizationDataPatternLayout extends PatternLayout { |
然后修改配置文件 logback.xml,修改其中 <encoder> 标签部分:
1 |
|
测试接口调用:
1 | ("/log") |
可以看到控制台输出内容,的确密码已经做了脱敏处理:
1 | print param: {password=123, username=admin} |
代码地址
本文示例代码地址:data-desensitization-demo