摘自Environment注释:
Properties play an important role in almost all applications, and may originate from a variety of sources: properties files, JVM system properties, system environment variables, JNDI, servlet context parameters, ad-hoc Properties objects, Maps, and so on. The role of the environment object with relation to properties is to provide the user with a convenient service interface for configuring property sources and resolving properties from them.
配置 XML方式 这种应该是最常见的方式了,在spring配置文件中:
1 <context:property-placeholder location ="classpath:bean.properties" />
注解方式 如果不是用xml方式,也可以使用注解方式,使用@PropertySource:
1 2 3 4 5 @Configuration @PropertySource("classpath:bean.properties") public class Application {}
其他方式 XML方式:
1 2 3 <bean class ="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer" > <property name ="locations" value ="classpath:bean.properties" /> </bean >
注解方式:
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Bean public static PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer propertyPlaceholderConfigurer () { PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer ppc = new PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer (); ppc.setLocation(new ClassPathResource ("bean.properties" )); return ppc; }
XML方式:
1 2 3 <bean class ="org.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer" > <property name ="locations" value ="classpath:bean.properties" /> </bean >
注解方式:
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Bean public static PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer propertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer () { PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer pspc = new PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer (); pspc.setLocation(new ClassPathResource ("bean.properties" )); return pspc; }
使用 XML 1 2 3 <bean id ="dataSource" > <property name ="url" value ="${jdbc.url}" /> </bean >
@Value 1 2 @Value("${jdbc.url}") private String url;
Environment 1 2 3 4 @Autowired private Environment env;... dataSource.setUrl(env.getProperty("jdbc.url" ));
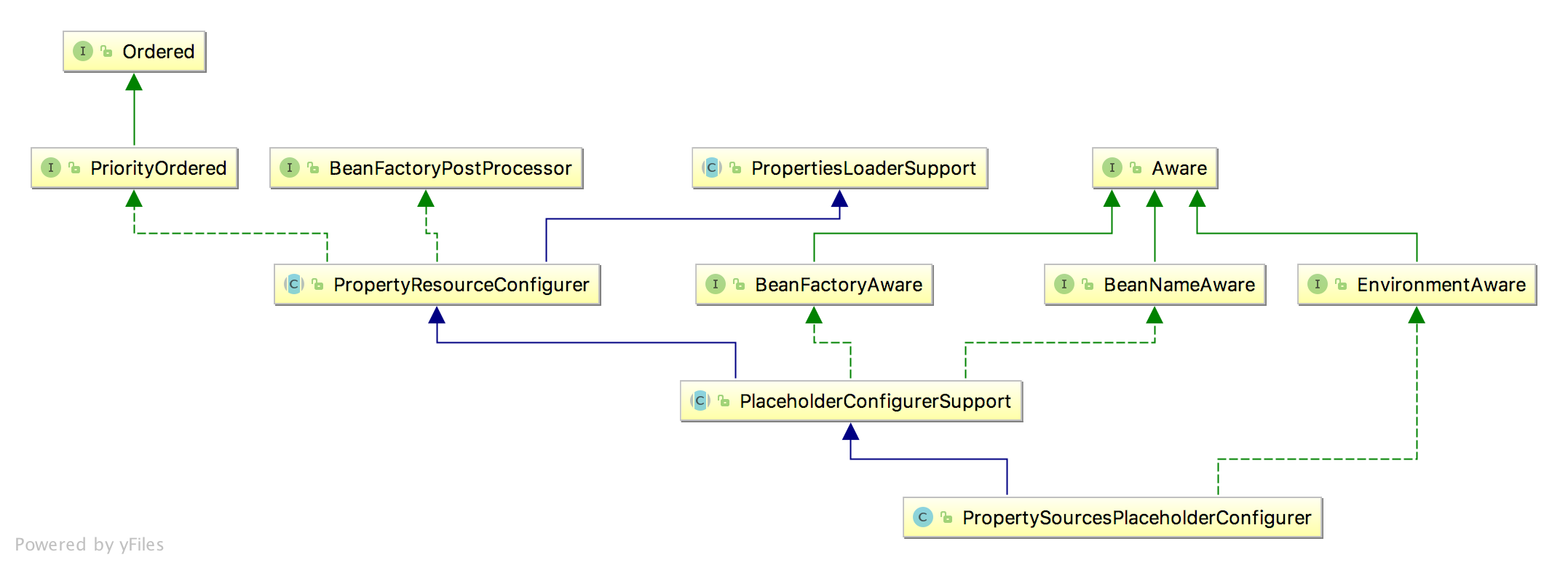
实现 在看实现xml中占位符替换之前,先看下PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer继承关系:
可以看到PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor,而其中的postProcessBeanFactory()方法可以对BeanDefinition做属性更改:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 @Override public void postProcessBeanFactory (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { if (this .propertySources == null ) { this .propertySources = new MutablePropertySources (); if (this .environment != null ) { this .propertySources.addLast( new PropertySource <Environment>(ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, this .environment) { @Override public String getProperty (String key) { return this .source.getProperty(key); } } ); } try { PropertySource<?> localPropertySource = new PropertiesPropertySource (LOCAL_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, mergeProperties()); if (this .localOverride) { this .propertySources.addFirst(localPropertySource); } else { this .propertySources.addLast(localPropertySource); } } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanInitializationException ("Could not load properties" , ex); } } processProperties(beanFactory, new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver (this .propertySources)); this .appliedPropertySources = this .propertySources; } protected void processProperties (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactoryToProcess, final ConfigurablePropertyResolver propertyResolver) throws BeansException { propertyResolver.setPlaceholderPrefix(this .placeholderPrefix); propertyResolver.setPlaceholderSuffix(this .placeholderSuffix); propertyResolver.setValueSeparator(this .valueSeparator); StringValueResolver valueResolver = new StringValueResolver () { @Override public String resolveStringValue (String strVal) { String resolved = ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders ? propertyResolver.resolvePlaceholders(strVal) : propertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(strVal); return (resolved.equals(nullValue) ? null : resolved); } }; doProcessProperties(beanFactoryToProcess, valueResolver); }
可以看到PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer在处理配置文件时,并没有将配置文件加入到environment,而是自己内部进行维护propertySource,因此无法通过environment中获取到配置文件内容
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 protected void doProcessProperties (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactoryToProcess, StringValueResolver valueResolver) { BeanDefinitionVisitor visitor = new BeanDefinitionVisitor (valueResolver); String[] beanNames = beanFactoryToProcess.getBeanDefinitionNames(); for (String curName : beanNames) { if (!(curName.equals(this .beanName) && beanFactoryToProcess.equals(this .beanFactory))) { BeanDefinition bd = beanFactoryToProcess.getBeanDefinition(curName); try { visitor.visitBeanDefinition(bd); } catch (Exception ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException (bd.getResourceDescription(), curName, ex.getMessage(), ex); } } } beanFactoryToProcess.resolveAliases(valueResolver); beanFactoryToProcess.addEmbeddedValueResolver(valueResolver); }
我们知道,Spring在注册Bean时会先将Bean转化为BeanDefinition,而这个BeanDefinition是未做任何属性上的处理(以例子来说,PropertiesService.name的值就是${properties.name}),而BeanDefinitionVisitor做的事就是将BeanDefinition的相关属性值做占位符替换处理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 public class BeanDefinitionVisitor { public void visitBeanDefinition (BeanDefinition beanDefinition) { visitParentName(beanDefinition); visitBeanClassName(beanDefinition); visitFactoryBeanName(beanDefinition); visitFactoryMethodName(beanDefinition); visitScope(beanDefinition); visitPropertyValues(beanDefinition.getPropertyValues()); ConstructorArgumentValues cas = beanDefinition.getConstructorArgumentValues(); visitIndexedArgumentValues(cas.getIndexedArgumentValues()); visitGenericArgumentValues(cas.getGenericArgumentValues()); } protected void visitGenericArgumentValues (List<ConstructorArgumentValues.ValueHolder> gas) { for (ConstructorArgumentValues.ValueHolder valueHolder : gas) { Object newVal = resolveValue(valueHolder.getValue()); if (!ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(newVal, valueHolder.getValue())) { valueHolder.setValue(newVal); } } } @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") protected Object resolveValue (Object value) { if (value instanceof BeanDefinition) { visitBeanDefinition((BeanDefinition) value); } else if (value instanceof BeanDefinitionHolder) { visitBeanDefinition(((BeanDefinitionHolder) value).getBeanDefinition()); } else if (value instanceof RuntimeBeanReference) { RuntimeBeanReference ref = (RuntimeBeanReference) value; String newBeanName = resolveStringValue(ref.getBeanName()); if (!newBeanName.equals(ref.getBeanName())) { return new RuntimeBeanReference (newBeanName); } } else if (value instanceof RuntimeBeanNameReference) { RuntimeBeanNameReference ref = (RuntimeBeanNameReference) value; String newBeanName = resolveStringValue(ref.getBeanName()); if (!newBeanName.equals(ref.getBeanName())) { return new RuntimeBeanNameReference (newBeanName); } } else if (value instanceof Object[]) { visitArray((Object[]) value); } else if (value instanceof List) { visitList((List) value); } else if (value instanceof Set) { visitSet((Set) value); } else if (value instanceof Map) { visitMap((Map) value); } else if (value instanceof TypedStringValue) { TypedStringValue typedStringValue = (TypedStringValue) value; String stringValue = typedStringValue.getValue(); if (stringValue != null ) { String visitedString = resolveStringValue(stringValue); typedStringValue.setValue(visitedString); } } else if (value instanceof String) { return resolveStringValue((String) value); } return value; } protected String resolveStringValue (String strVal) { if (this .valueResolver == null ) { throw new IllegalStateException ("No StringValueResolver specified - pass a resolver " + "object into the constructor or override the 'resolveStringValue' method" ); } String resolvedValue = this .valueResolver.resolveStringValue(strVal); return (strVal.equals(resolvedValue) ? strVal : resolvedValue); } }
可以看到visitBeanDefinition()对很多属性都做了占位符替换,每个属性替换方法实现都类似。以例子来说,通过构造方法属性注入,所以看visitGenericArgumentValues(),该方法实现也是比较简单,循环获取每个属性对应的属性值(${properties.name}),然后调用PropertyResolver实现占位符替换,最后对属性重新设值
context:property-placeholder context:property-placeholder看下解析注册部分,因为占位符替换逻辑其实就是通过注册PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer实现,部分代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 @Override public final BeanDefinition parse (Element element, ParserContext parserContext) { AbstractBeanDefinition definition = parseInternal(element, parserContext); if (definition != null && !parserContext.isNested()) { try { BeanDefinitionHolder holder = new BeanDefinitionHolder (definition, id, aliases); registerBeanDefinition(holder, parserContext.getRegistry()); } catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { parserContext.getReaderContext().error(ex.getMessage(), element); return null ; } } return definition; }
parseInternal()在子类AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser中实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 protected final AbstractBeanDefinition parseInternal (Element element, ParserContext parserContext) { BeanDefinitionBuilder builder = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(); String parentName = getParentName(element); if (parentName != null ) { builder.getRawBeanDefinition().setParentName(parentName); } Class<?> beanClass = getBeanClass(element); if (beanClass != null ) { builder.getRawBeanDefinition().setBeanClass(beanClass); } return builder.getBeanDefinition(); }
看下getBeanClass()方法,决定了AbstractBeanDefinition类型:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @Override protected Class<?> getBeanClass(Element element) { if (SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_DEFAULT.equals(element.getAttribute(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_ATTRIBUTE))) { return PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer.class; } return PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer.class; }
在BeanFactory中注册了PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer之后,占位符替换的逻辑就和上面一样了
@PropertySources ConfigurationClassParser在注解启动时(使用@Configuration)是一个非常重要的类,功能就是解析使用@Configuration的配置类,包括@PropertySources,@ComponentScan等类注解,以及@Bean等方法注解,此处看下@PropertySources解析:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass (ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass) throws IOException { for (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable( sourceClass.getMetadata(), PropertySources.class, org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource.class)) { if (this .environment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) { processPropertySource(propertySource); } else { logger.warn("Ignoring @PropertySource annotation on [" + sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName() + "]. Reason: Environment must implement ConfigurableEnvironment" ); } } return null ; } private void processPropertySource (AnnotationAttributes propertySource) throws IOException { String name = propertySource.getString("name" ); String[] locations = propertySource.getStringArray("value" ); boolean ignoreResourceNotFound = propertySource.getBoolean("ignoreResourceNotFound" ); Assert.isTrue(locations.length > 0 , "At least one @PropertySource(value) location is required" ); for (String location : locations) { try { String resolvedLocation = this .environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(location); Resource resource = this .resourceLoader.getResource(resolvedLocation); ResourcePropertySource rps = (StringUtils.hasText(name) ? new ResourcePropertySource (name, resource) : new ResourcePropertySource (resource)); addPropertySource(rps); } catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) { if (!ignoreResourceNotFound) { throw ex; } } catch (FileNotFoundException ex) { if (!ignoreResourceNotFound) { throw ex; } } } }
因此,在这种配置下,资源文件中的内容可以通过注入Environment获取:
1 2 3 4 5 @Autowired private Environment env;... dataSource.setUrl(env.getProperty("jdbc.url" ));
参考 Properties with Spring